A cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or a stroke is a medical condition where the blood circulation in the brain is suddenly disrupted. 17 million people worldwide suffer from a stroke each year, making it the second most common cause of death and the leading cause of adult disability. Strokes can be divided into ischemic strokes and hemorrhagic strokes.
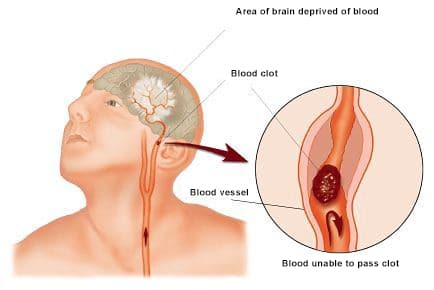
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows the arteries supplying blood and oxygen to the brain. Consequently, the brains get too little or no oxygen and can be permanently damaged.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) or a “mini stroke” is caused by a temporay blockage. The blood clot that gets stuck, eventually breaks up or moves on by itself. The symptoms of a stroke, such as paralysis, dizziness or double vision, will fade away when the blood clot breaks free again and the blocked part of the brain gets oxygen and nutrient rich blood again.
It is important that anyone who suffered from a TIA consults a doctor as soon as possible to determine the cause of this mini stroke.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks or bursts. That causes blood to pile up in the brain and damages brain cells.
Cardiac arrhythmias and stroke
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common cardiac arrhythmias and increases the risk of a stroke up to 5 times. Although a patient frequently does not suffer from any symptoms, it is important that the arrhythmia gets discovered and treated as quickly as possible. When the blood isn’t pumped through the heart effectively, as is the case in atrial fibrillation, blood clots can form and eventually cause a stroke.
When you suffer from atrial fibrillation the upper chambers of the heart start vibrating very fast, which disturbes the normal pumping function of the atria. The blood flow in the atria reduces which causes a standstill of the blood and can eventually lead to the formation of blood clots. These blood clots can be carried along in the blood circulation and end up in the brain. When a blood clot gets stuck the brain it causes a stroke or cerebral infarction.
Other causes
17 million people suffer stroke worldwide each year. A whopping 20% of these strokes are caused by atrial fibrillation, the other 80% can be generated by other factors, such as:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Cardiovascular disease
- Obesity
- Prolonged stress
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Low physical activity
- Unhealthy diet
How to recognise a stroke
The symptoms of a stroke depend on the brain area in which the blood flow is disturbed and the size of that area.

Some possible symptoms include:
- Sudden paralysis of an arm or leg, usually only on one side of the body;
- A crooked mouth;
- Blindness or diplopia;
- Struggling with eating or swallowing;
- No longer being able to speak or understanding words;
- Balance disorder and dizziness;
- Tingling or numbness.
How to react when you think someone is having a stroke
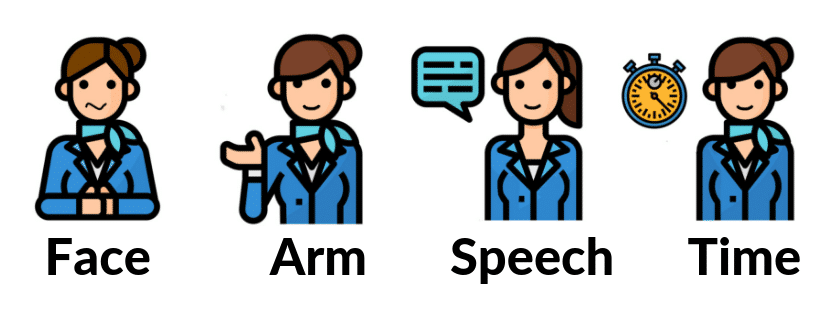
If you think someone is having a stroke, it is important to recognize the symptoms. This can be done using the FAST-test:
- Face: Ask the victim to smile. If the mouth is crooked or one side of the face is drooping, this could indicate a stroke;
- Arm: Ask the victim to stick out both arms and check whether they go up at once. If not, this may indicate a stroke;
- Speech: Listen if the victim speaks unclear, can’t get his words out or has difficulty understanding you;
- Time: Determine how long the symptoms maintain. Call in medical help as soon as possible to limit the damage.
If the victim tests positive for the above, contact 911 immediately. The sooner a stroke can be treated, the more limited the brain damage is and the greater the chance for recovery.
The impact of a stroke
Some people recover completely after a stroke, but unfortunately approximately 1 in 3 victims experience lasting limitations. A stroke can entail physical, psychological or social consequences.
Common consequences include:
- Signs of paralysis;
- Loss of vision;
- Disturbance in perception;
- Speech disorder;
- Concentration problems;
- Exhaustion;
- Slowdown of the thinking process;
- Disturbance in behaviour, emotions and or thinking.
A stroke does not only affect the victim but also his or her surroundings.
How to prevent a stroke
There are certain characteristics, habits and lifestyles that may increase the risk of a stroke. As with atrial fibrillation (AF) the risk of stroke grows as you become older. Fortunately, there are a lot of factors that we control ourselves, like:
- Quit smoking;
- Moderate your alcohol consumption;
- Check your blood pressure regularly;
- Have your cholesterol checked out regularly from the age of 40;
- Have your blood sugar checked out regularly from the age of 45;
- Get plenty of exercise;
- Eat as healthy as possible;
- Report an irregular pulse or palpitation to your doctor. You can easily check your heart rhythm at home using the FibriCheck-app.
Created on October 16th, 2019 at 01:30 pm
Last updated on January 11th, 2023 at 09:26 am





